-
[AWS] Relational Database Service (RDS)
A distributed relational database service, a web service running "in the cloud" designed to simplify the setup, operation, and scaling of a relational database for use in applications.
-
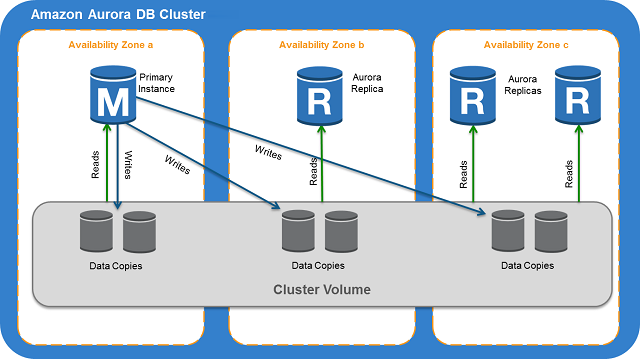
[AWS] Aurora
A MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible relational database built for the cloud, that combines the performance and availability of traditional enterprise databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open source databases.
-
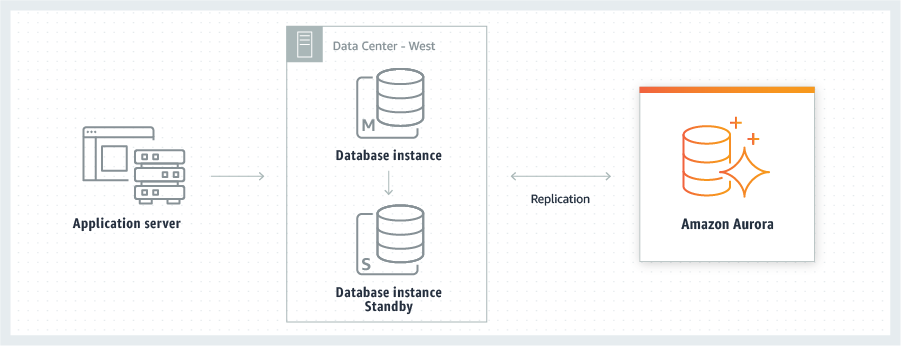
[Azure] SQL Server
A managed cloud database (formerly SQL Azure, SQL Server Data Services, SQL Services, and Windows Azure SQL Database).
-
[Google Cloud] SQL
Fully managed relational database service for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL server.
-
[Google Cloud] Spanner
A NewSQL database providing global transactions, strongly consistent reads, and automatic multi-site replication and failover.
-
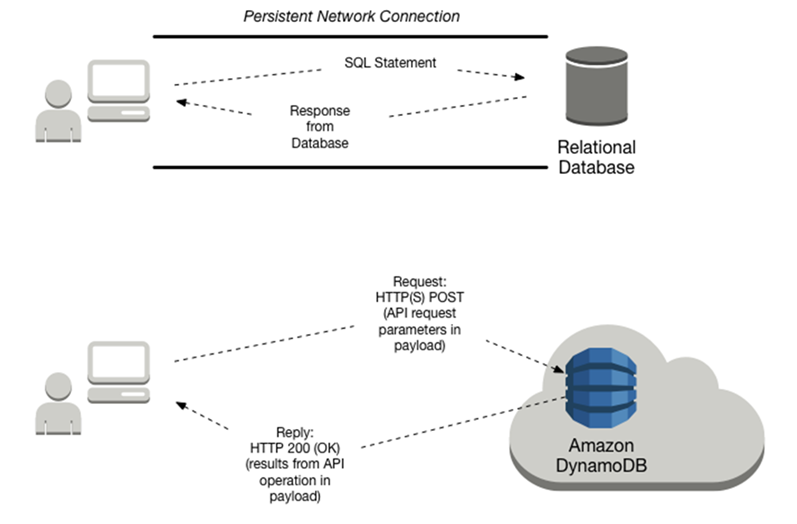
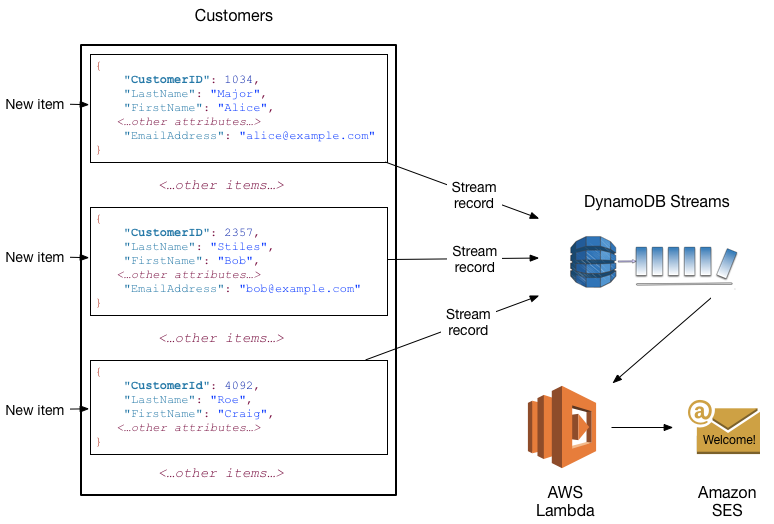
[AWS] DynamoDB
A fully managed proprietary NoSQL database service that supports key-value and document data structures.
-
[Google Cloud] Datastore (deprecated)
Cloud Datastore is a highly-scalable NoSQL database for your web and mobile applications.
-
[Google Cloud] Firestore
Store cloud-native app data at global scale.
-
[Azure] Table Storage
A service that stores structured NoSQL data in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design.
-
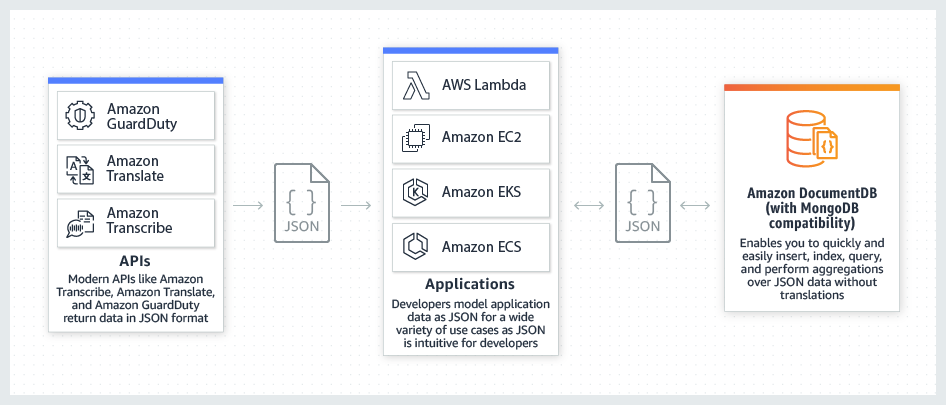
[AWS] DocumentDB
Fast, scalable, highly available MongoDB-compatible database service.
-
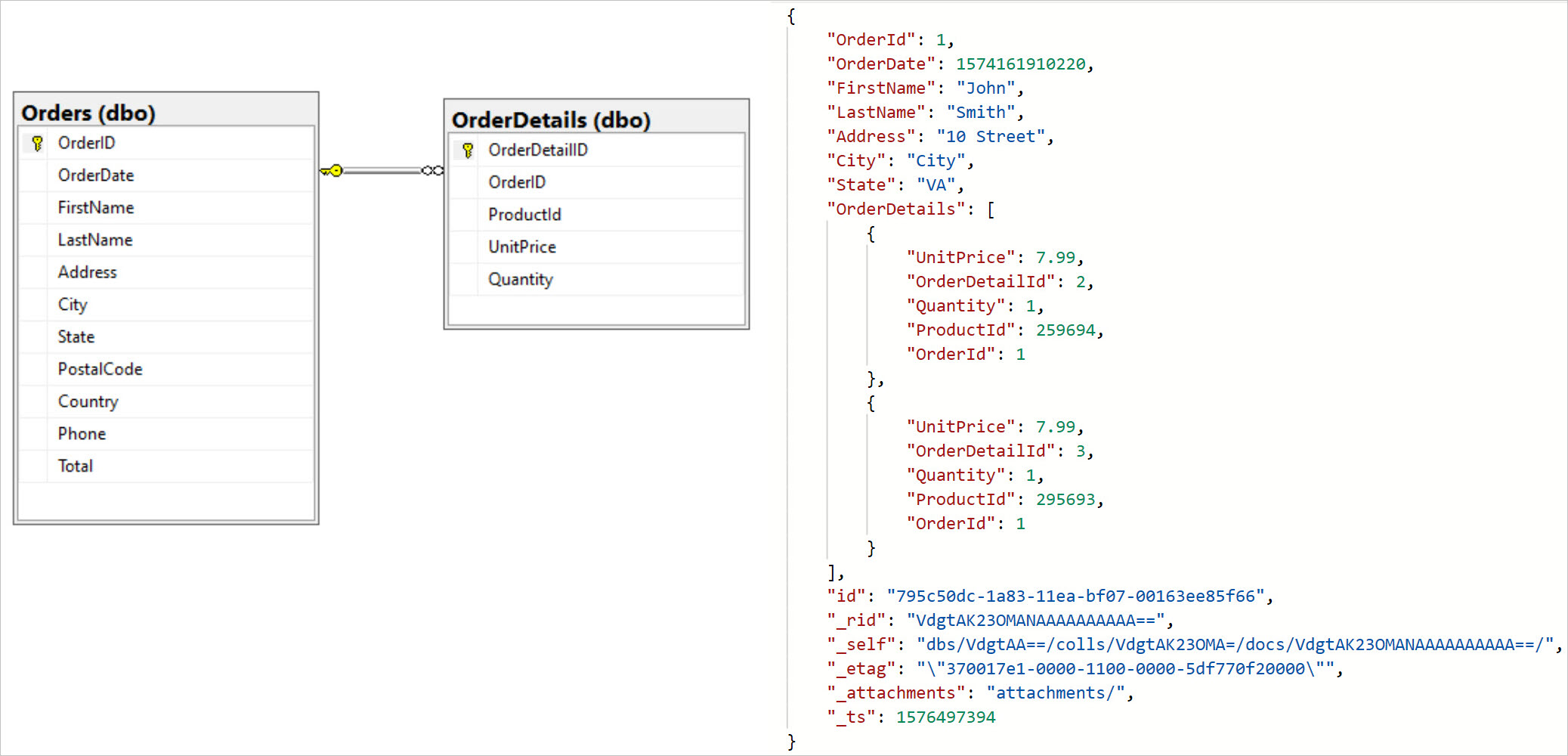
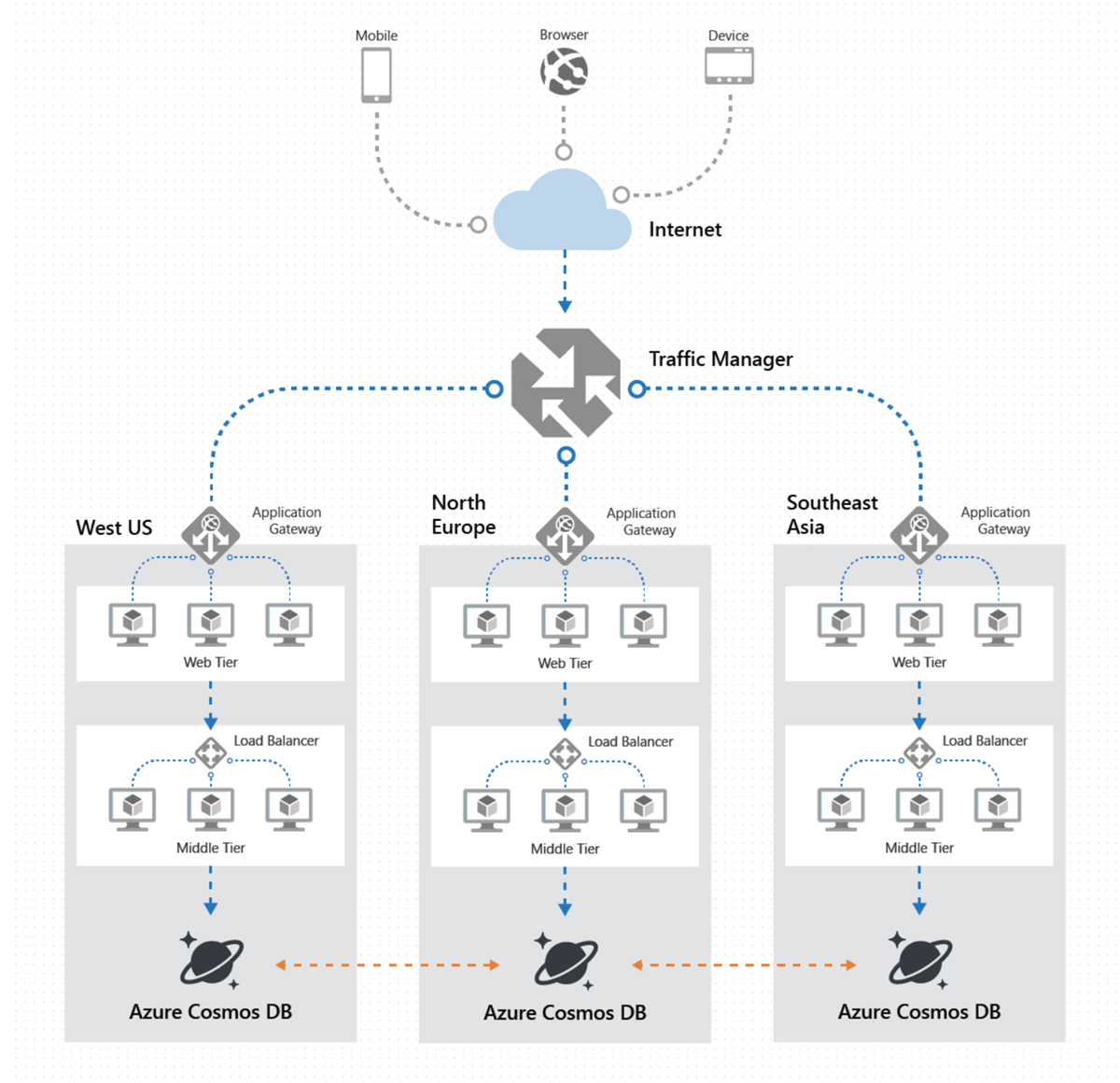
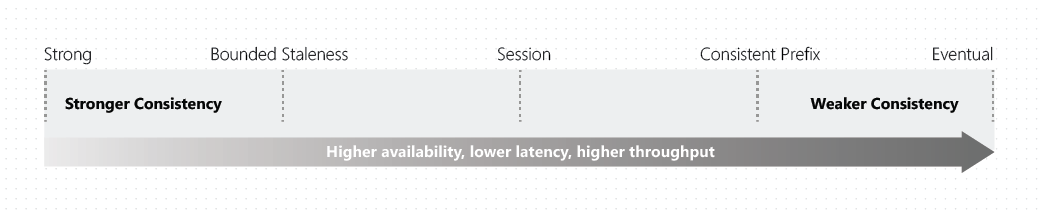
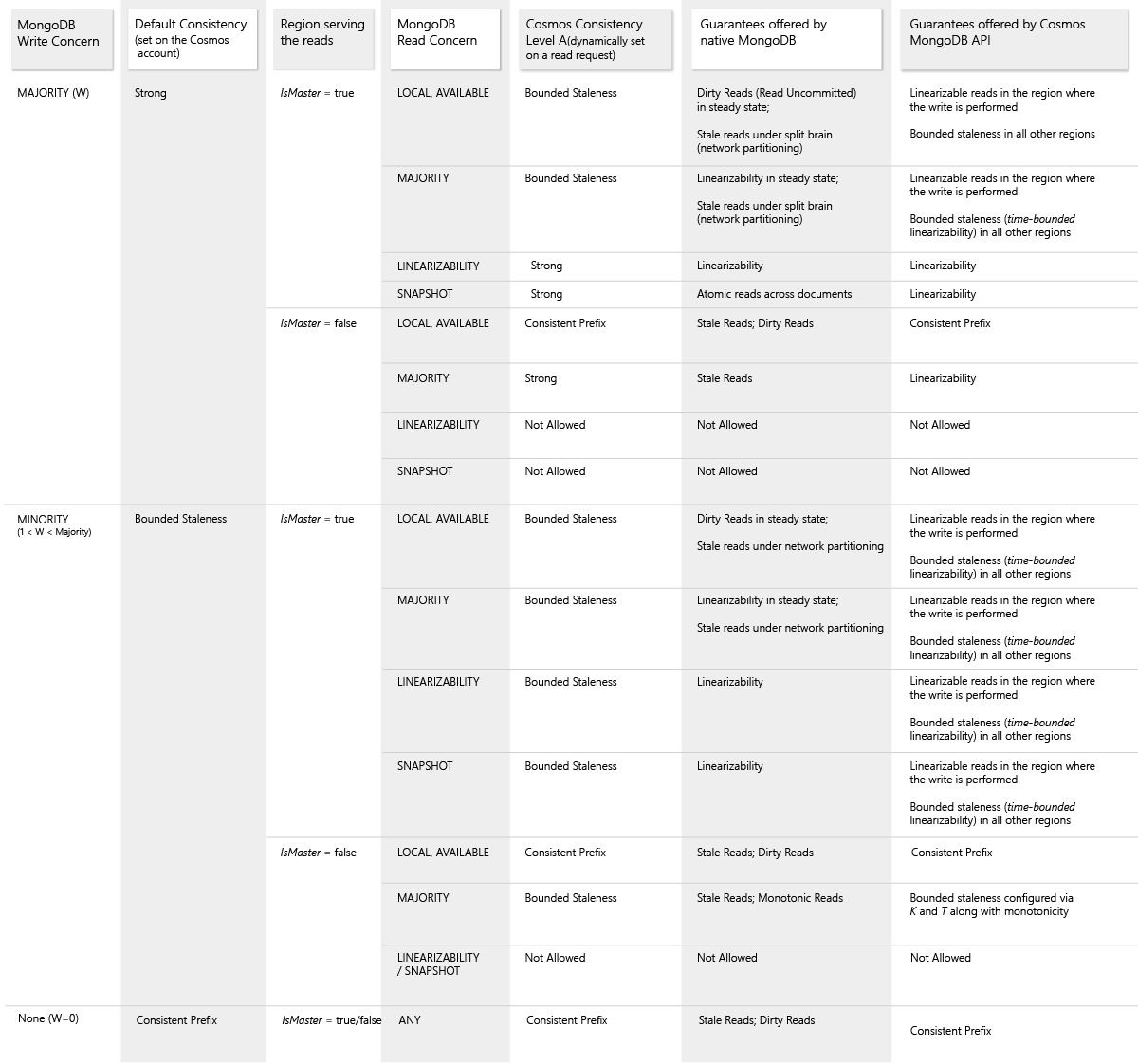
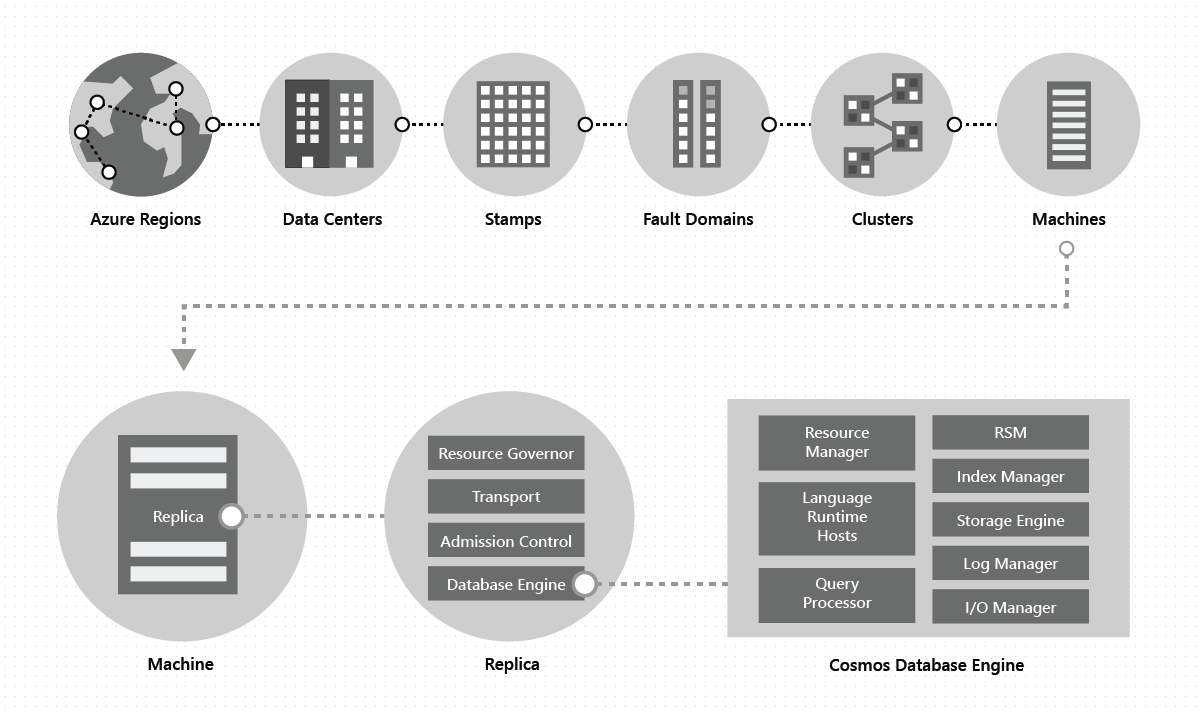
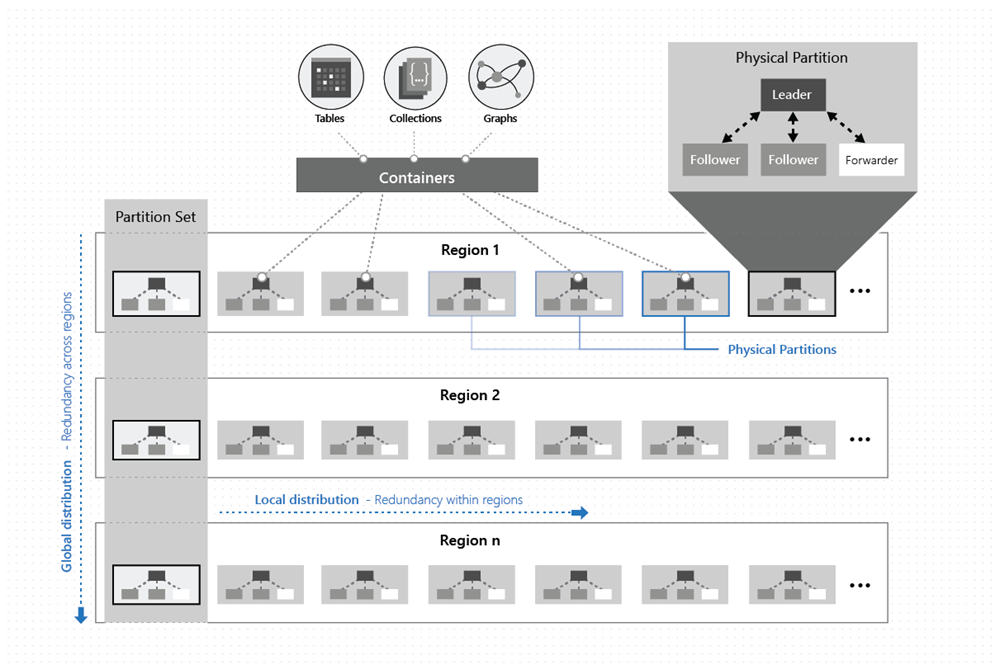
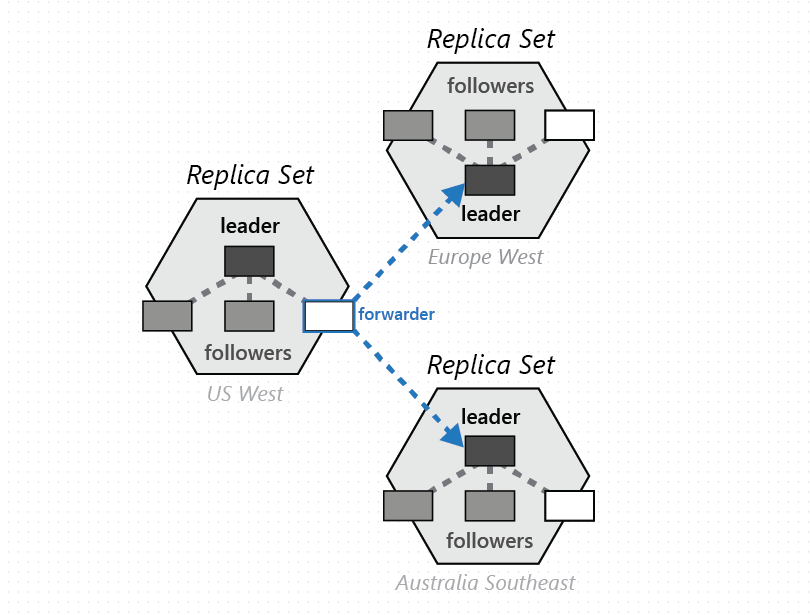
[Azure] Cosmos DB
Globally-distributed, multi-model database service "for managing data at planet-scale".
-
[Google Cloud] Bigtable
A petabyte-scale, fully managed NoSQL database service for large analytical and operational workloads.
-
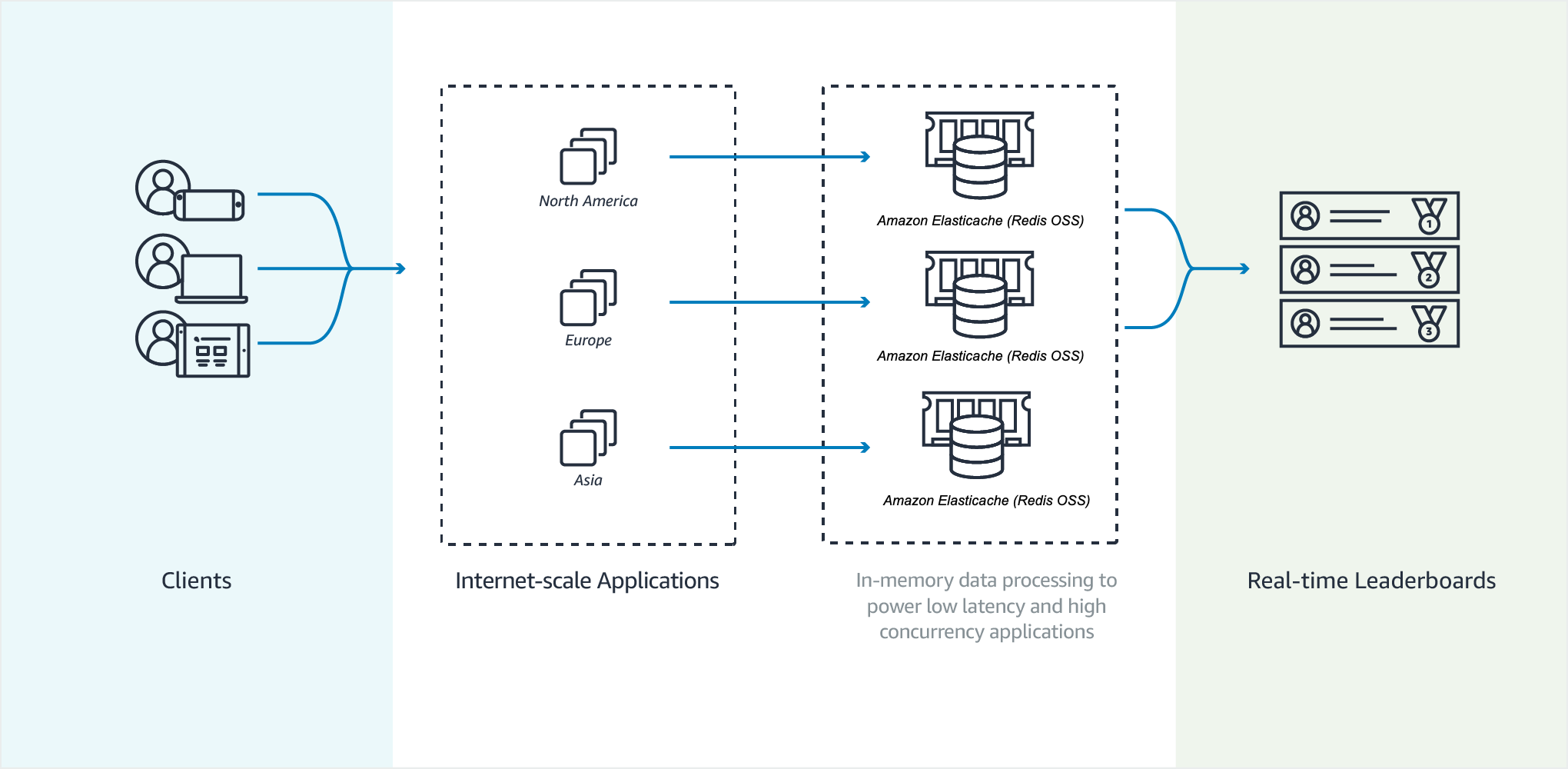
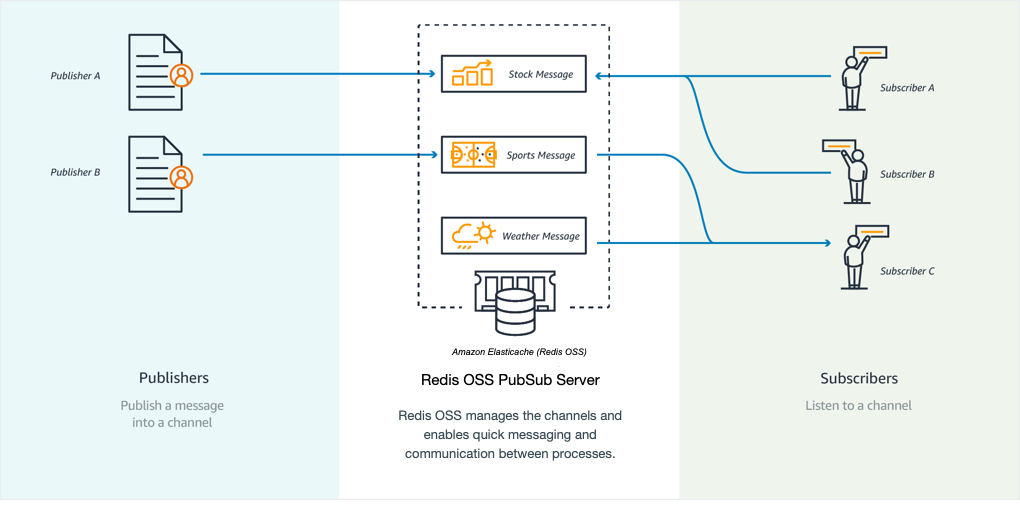
[AWS] ElastiCache for Redis
Redis compatible in-memory data store built for the cloud. Power real-time applications with sub-millisecond latency.
-
[AWS] ElastiCache for Memcached
Managed, Memcached-compatible, in-memory store. Sub-millisecond latency to power real-time applications.
-
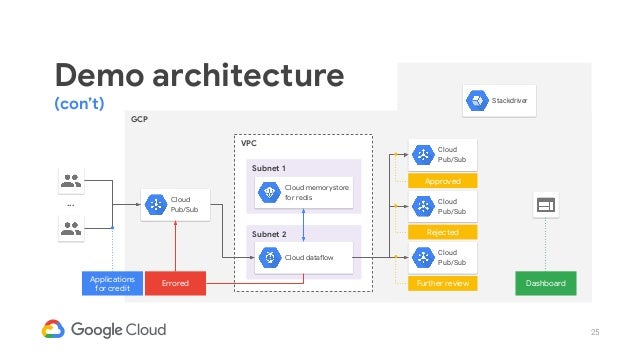
[Google Cloud] Memorystore
Fully managed in-memory data store service for Redis and Memcached.
-
[Azure] Cache for Redis
Fully managed, open source–compatible in-memory data store to power fast, scalable applications.
-
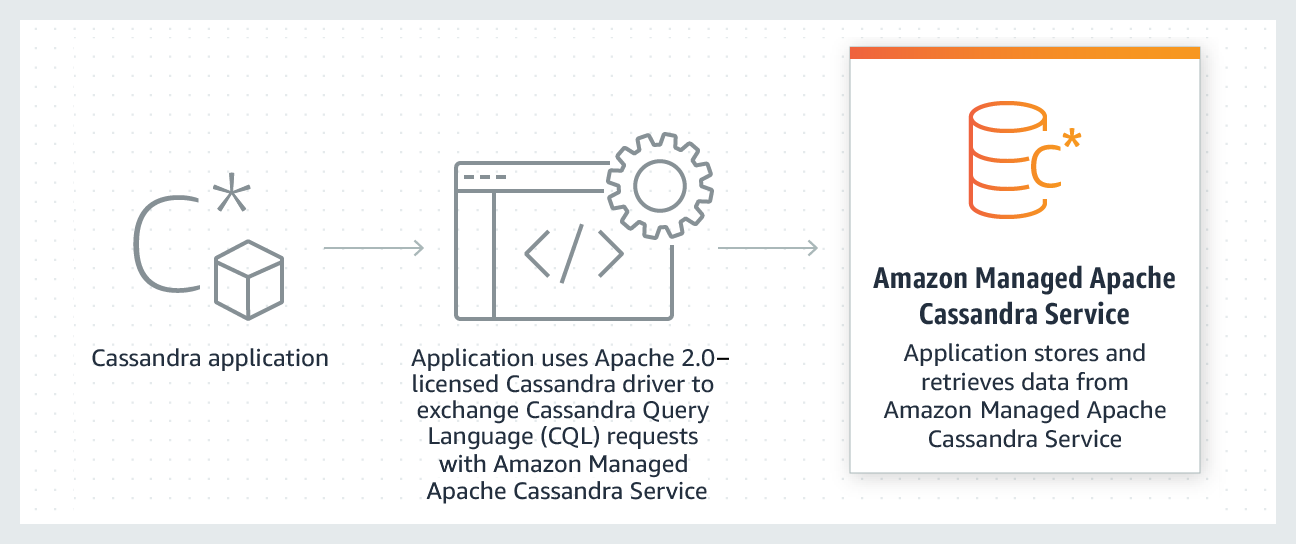
[AWS] Managed Apache Cassandra Service
A scalable, highly available, and managed Apache Cassandra–compatible database service.
-
[AWS] Keyspaces
A scalable, highly available, and managed Apache Cassandra–compatible database service.
-
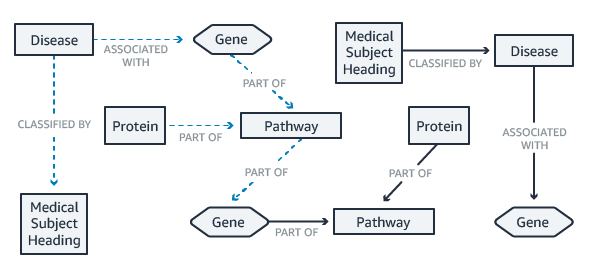
[AWS] Neptune
A fast, reliable, fully managed graph database service that makes it easy to build and run applications that work with highly connected datasets.
-
[AWS] Timestream
A fast, scalable, fully managed time series database service for IoT and operational applications that makes it easy to store and analyze trillions of events per day at 1/10th the cost of relational databases.
-
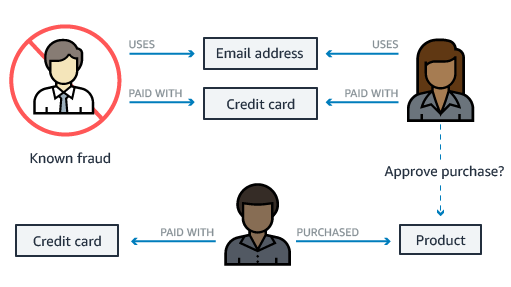
[AWS] Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB)
Fully managed ledger database that provides a transparent, immutable, and cryptographically verifiable transaction log. Owned by a central trusted authority.
-
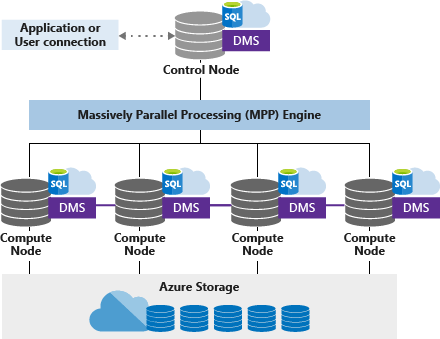
[AWS] Redshift
The most popular and fastest cloud data warehouse.
-
Google BigQuery
A serverless, highly scalable, and cost-effective cloud data warehouse designed to help you make informed decisions quickly, so you can transform your business with ease.
-
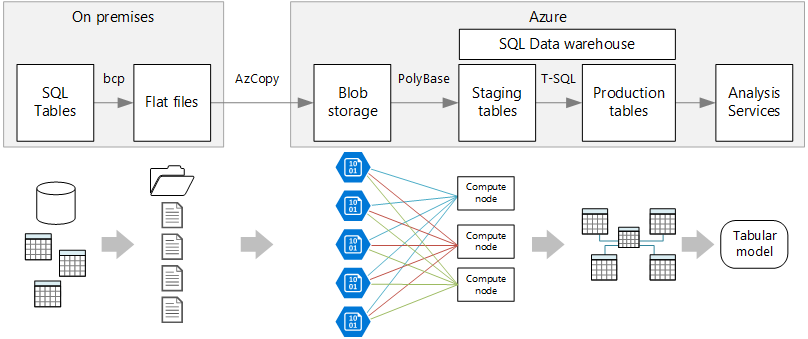
[Azure] Synapse Analytics (formerly SQL Data Warehouse)
Limitless analytics service with unmatched time to insight.
-
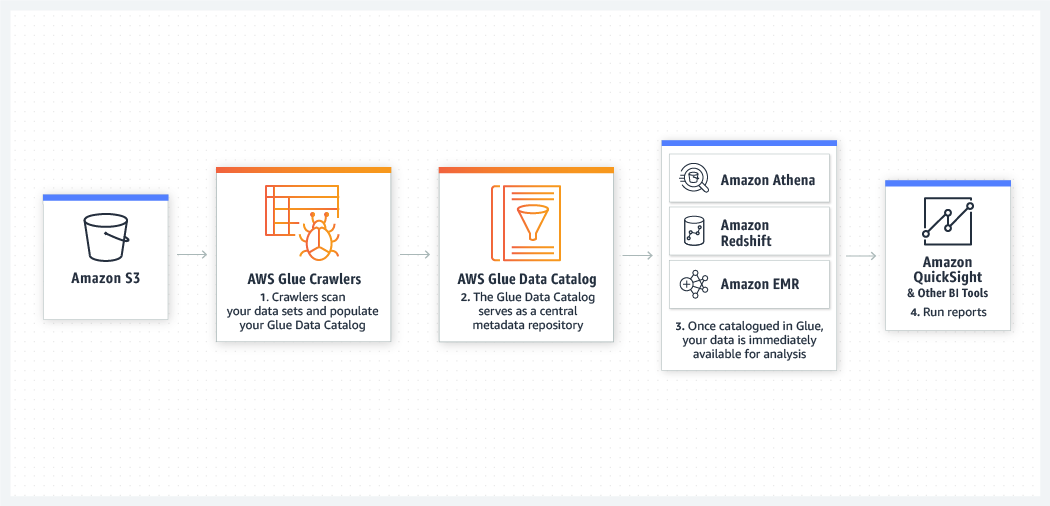
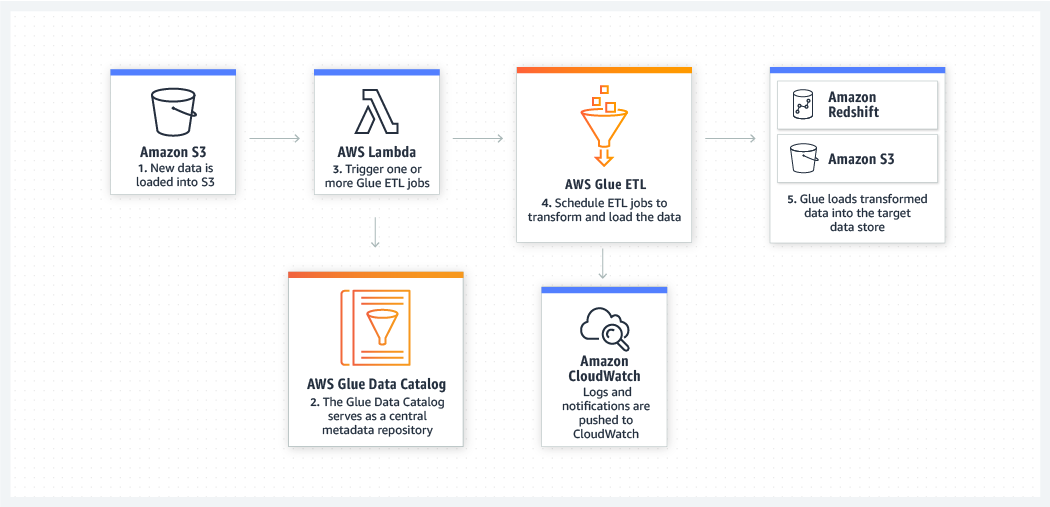
[AWS] Glue
Simple, flexible, and cost-effective ETL.
-
[Google Cloud] Data Fusion
Fully managed, code-free data integration at any scale.
-
[Azure] Data Factory
Hybrid data integration service that simplifies ETL at scale.
-
[AWS] Elastic MapReduce (EMR)
Easily run and scale Apache Spark, Hadoop, HBase, Presto, Hive, and other big data frameworks.
-
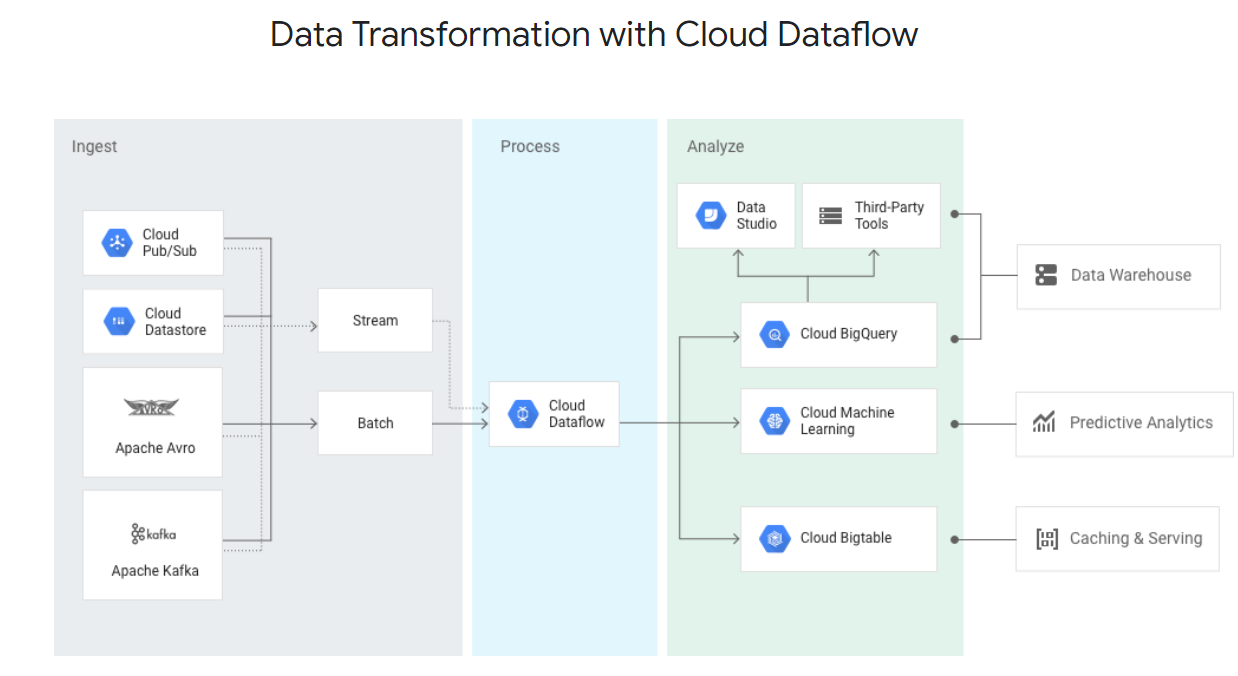
Google Dataflow
Fast, unified stream and batch data processing.
-
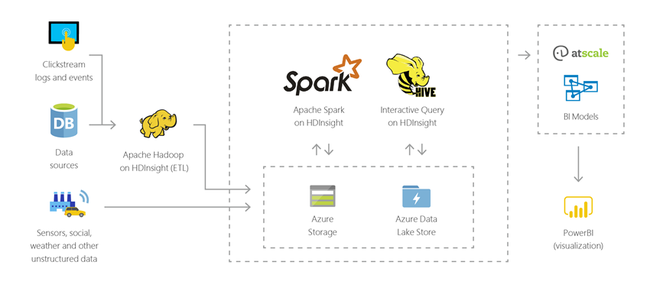
[Azure] HD Insight
Easy, cost-effective, enterprise-grade service for open source analytics.
-
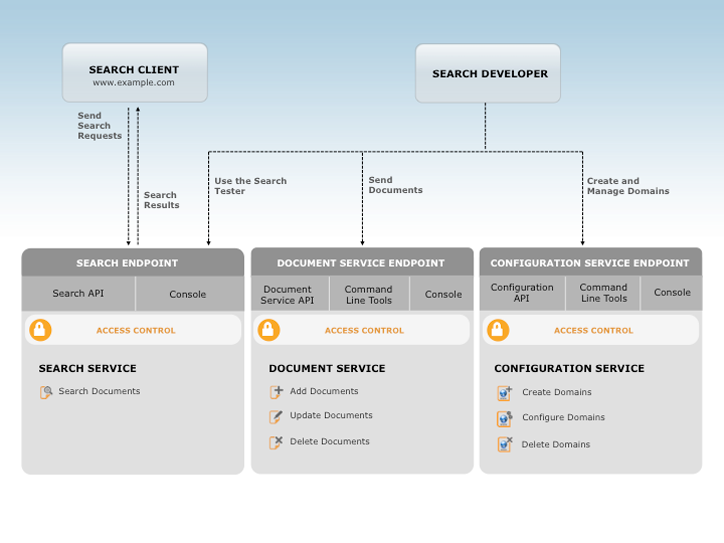
[AWS] CloudSearch
A managed service in the AWS Cloud that makes it simple and cost-effective to set up, manage, and scale a search solution for your website or application.
-
[AWS] Elasticsearch Service
A fully managed service that makes it easy for you to deploy, secure, and run Elasticsearch cost effectively at scale.
-
[Google Cloud] Search
With 100+ connectors, you can index your third-party content from dozens of enterprise sources.
-
[Azure] Cognitive Search
A search-as-a-service cloud solution that gives developers APIs and tools for adding a rich search experience over private, heterogeneous content in web, mobile, and enterprise applications.
-
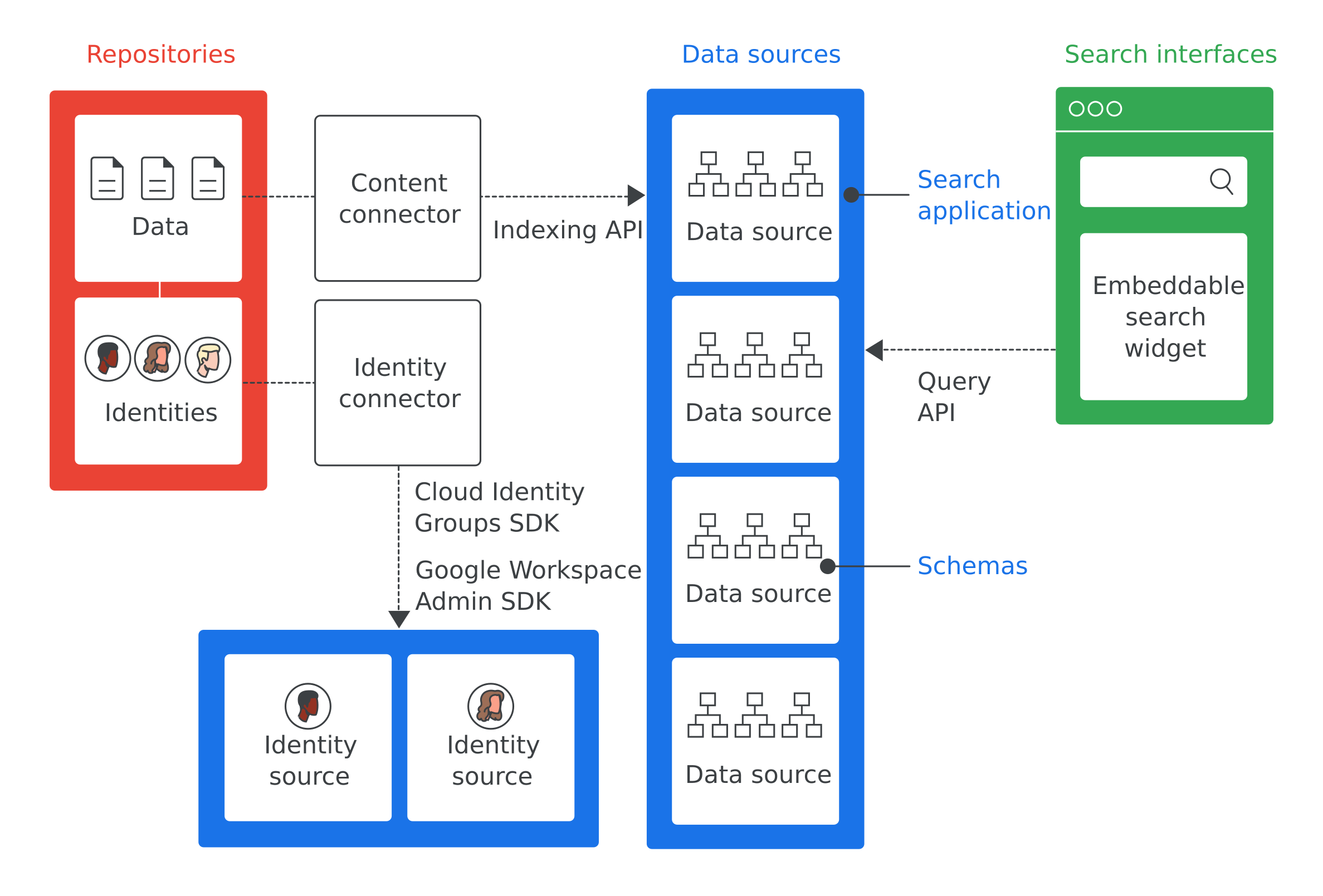
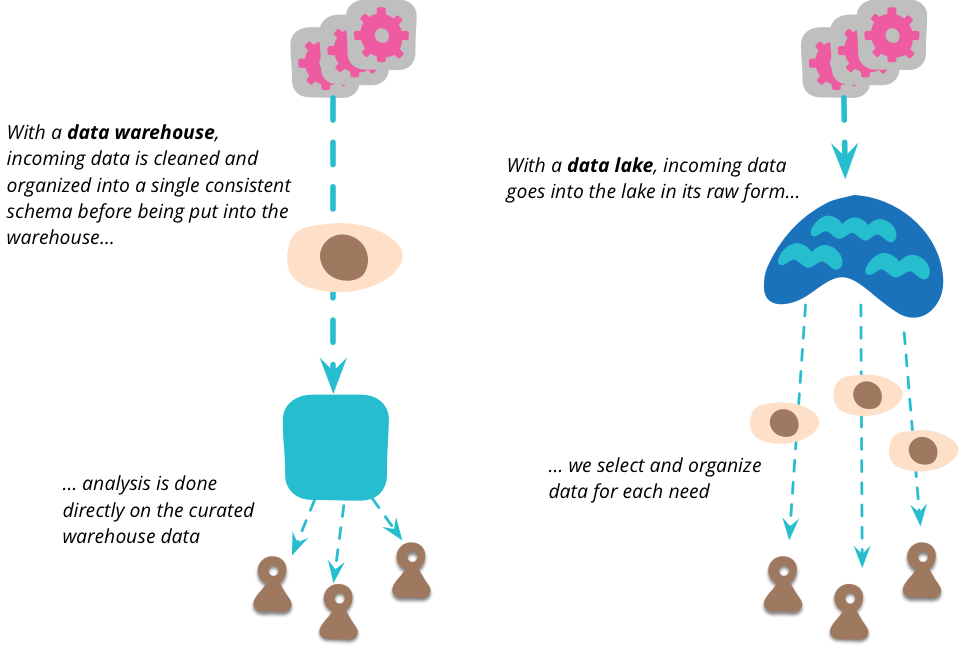
Data Lake on AWS
A data lake solution that automatically configures the core AWS services necessary to easily tag, search, share, transform, analyze, and govern specific subsets of data across a company or with other external users.
-
Cloud Storage as a Data Lake
A serverless, highly scalable, and cost-effective cloud data warehouse designed to help you make informed decisions quickly, so you can transform your business with ease.
-
[Azure] Data Lake
A no-limits data lake to power intelligent action.